Translation Google
Invasive meningococcal infections: increase in cases in France in 2023
Public Health France is publishing its annual surveillance data for invasive meningococcal infections in 2023, marked by an increase in the number of reported cases and contrasting developments for the different serogroups and age groups.
Published on April 9, 2024
Invasive meningococcal infections ( IIM) are bacterial infections caused by meningococcus. They are very serious and can cause meningitis or septicemia. Public Health France monitors the evolution of the epidemiological situation in France and publishes each year a report on this surveillance which is essential to detect any unusual situation.
The 2023 report shows a resurgence of cases with a sharp increase in IIMs W and Y to levels never observed before, marking significant changes in the epidemiology of IIMs following the COVID-19 pandemic . These results point to the age groups most at risk of infection and underline the challenge of achieving high vaccination coverage in the groups targeted by meningococcal vaccination recommendations.
The data from this surveillance were useful for the work of the High Authority for Health on the revision of the vaccination strategy against meningococci.
An early peak in the number of cases of invasive meningococcal infections during winter 2022-2023
After several years of low incidence, the 2022-2023 winter season was marked by an early and very high peak in IIM cases (including 89 cases in December 2022 and 80 cases in January 2023 ). The monthly number of cases remained at high levels throughout the first half of 2023 before returning to levels comparable to pre-pandemic years from the second half of the year.
In 2023, 560 cases of invasive meningococcal infections were reported, an increase of 72% compared to 2022. Among them, 44% were linked to serogroup B, 29% to serogroup W and 24% to serogroup Y. The presence of purpura fulminans was reported in the majority of reported cases (23% for IIM B, 16% for IIM W and 11% for IIM Y).
Infants and young children remained at highest risk of B-MI. W-MI affected both infants and adults of different age groups while Y-IMD was more common in the elderly but also affected adults. the youngest.
The incidence rates of reported cases varied depending on the region of residence .
Number of cases of invasive meningococcal infections according to the main serogroups, France as a whole, 2016-2023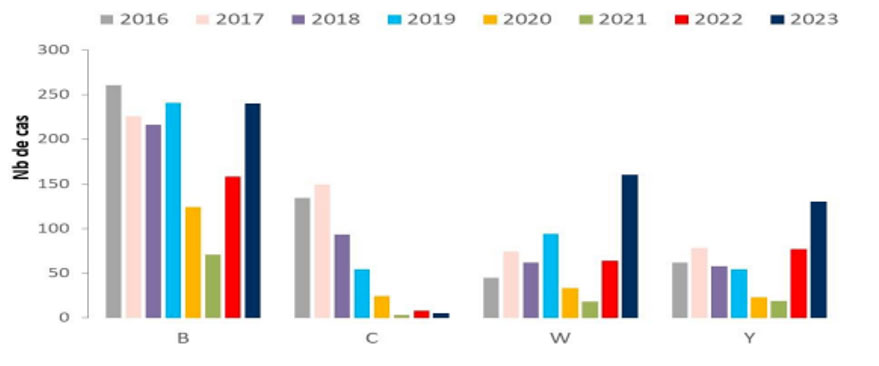
Contrasting developments for certain types of invasive meningococcal infections
Among the four existing serogroups, IIM Bs have the most cases with 240 cases in 2023, followed by IIM W (160), IIM Y (130), while IIM C have become rare (5).
Sharp increase in IIM W and IIM Y to levels never seen before
For serogroups B/W/Y, the number of cases of invasive meningococcal infections increased sharply among adults aged 25 and over, while the rebound in 2022 was initially observed among young adults aged 15-24. years. The increase in 2023 was particularly marked among people aged 60 and over. IIM W were associated with high case fatality (19% with 31 deaths) compared to other serogroups (7% for IIM B and 8% for IIM Y).
In infants under 1 year old and children aged 1 to 4 years, IIM B remained in the majority representing almost 60% of cases but slightly lower in 2022 (67%), while IIM Y and W represented a growing share of cases with 41% of cases among those under 5 years old (vs. 30% in 2022). Among those over 15 years old, IIM W and Y increased with age. Elderly people were most affected by IIM Y.
This post-COVID-19 resurgence could be explained by the decline in immunity in the population less exposed to meningococci during the pandemic, but also by the return of respiratory viruses (in particular influenza ) which can promote invasive bacterial infections. Furthermore, the different evolution depending on age could reflect a reintroduction of meningococci having first affected young adults in whom carriage is more frequent, followed by transmission to older age groups.
Vaccination and evolution of the vaccination strategy against meningococci
Vaccination against serogroup C meningococcal infections has been recommended since 2010 in infants and catch-up up to the age of 24. Vaccination against invasive meningococcal serogroup B infections has been recommended since 2022 for all infants. There are also specific recommendations for people at risk or specific situations.
...
Invasive meningococcal infections: increase in cases in France in 2023
Public Health France is publishing its annual surveillance data for invasive meningococcal infections in 2023, marked by an increase in the number of reported cases and contrasting developments for the different serogroups and age groups.
Published on April 9, 2024
Invasive meningococcal infections ( IIM) are bacterial infections caused by meningococcus. They are very serious and can cause meningitis or septicemia. Public Health France monitors the evolution of the epidemiological situation in France and publishes each year a report on this surveillance which is essential to detect any unusual situation.
The 2023 report shows a resurgence of cases with a sharp increase in IIMs W and Y to levels never observed before, marking significant changes in the epidemiology of IIMs following the COVID-19 pandemic . These results point to the age groups most at risk of infection and underline the challenge of achieving high vaccination coverage in the groups targeted by meningococcal vaccination recommendations.
The data from this surveillance were useful for the work of the High Authority for Health on the revision of the vaccination strategy against meningococci.
An early peak in the number of cases of invasive meningococcal infections during winter 2022-2023
After several years of low incidence, the 2022-2023 winter season was marked by an early and very high peak in IIM cases (including 89 cases in December 2022 and 80 cases in January 2023 ). The monthly number of cases remained at high levels throughout the first half of 2023 before returning to levels comparable to pre-pandemic years from the second half of the year.
In 2023, 560 cases of invasive meningococcal infections were reported, an increase of 72% compared to 2022. Among them, 44% were linked to serogroup B, 29% to serogroup W and 24% to serogroup Y. The presence of purpura fulminans was reported in the majority of reported cases (23% for IIM B, 16% for IIM W and 11% for IIM Y).
Infants and young children remained at highest risk of B-MI. W-MI affected both infants and adults of different age groups while Y-IMD was more common in the elderly but also affected adults. the youngest.
The incidence rates of reported cases varied depending on the region of residence .
Number of cases of invasive meningococcal infections according to the main serogroups, France as a whole, 2016-2023

Contrasting developments for certain types of invasive meningococcal infections
Among the four existing serogroups, IIM Bs have the most cases with 240 cases in 2023, followed by IIM W (160), IIM Y (130), while IIM C have become rare (5).
Sharp increase in IIM W and IIM Y to levels never seen before
For serogroups B/W/Y, the number of cases of invasive meningococcal infections increased sharply among adults aged 25 and over, while the rebound in 2022 was initially observed among young adults aged 15-24. years. The increase in 2023 was particularly marked among people aged 60 and over. IIM W were associated with high case fatality (19% with 31 deaths) compared to other serogroups (7% for IIM B and 8% for IIM Y).
In infants under 1 year old and children aged 1 to 4 years, IIM B remained in the majority representing almost 60% of cases but slightly lower in 2022 (67%), while IIM Y and W represented a growing share of cases with 41% of cases among those under 5 years old (vs. 30% in 2022). Among those over 15 years old, IIM W and Y increased with age. Elderly people were most affected by IIM Y.
This post-COVID-19 resurgence could be explained by the decline in immunity in the population less exposed to meningococci during the pandemic, but also by the return of respiratory viruses (in particular influenza ) which can promote invasive bacterial infections. Furthermore, the different evolution depending on age could reflect a reintroduction of meningococci having first affected young adults in whom carriage is more frequent, followed by transmission to older age groups.
Vaccination and evolution of the vaccination strategy against meningococci
Vaccination against serogroup C meningococcal infections has been recommended since 2010 in infants and catch-up up to the age of 24. Vaccination against invasive meningococcal serogroup B infections has been recommended since 2022 for all infants. There are also specific recommendations for people at risk or specific situations.
...