Translation Google
Outbreak of suspected cases of Monkeypox in the DRC: more than 220 notifications in one week
Wednesday March 27, 2024 - 2:53 p.m.
The Monkeypox coordination of the Ministry of Health specified in its report that it had notified 228 new suspected cases of Monkeypox during epidemiological week 11 (March 15 to 22, 2024).
“228 new suspected cases and 8 deaths reported (case fatality = 3.5%) in SE 11 of 2024. Seven out of 27 provincial health divisions reported cases, or 27%. The ZS of Lotumbe in the province of Équateur reported the highest number of cases in S11, i.e. 85 cases and 1 death (case fatality = 1.2%), followed by Budjala, in Sud-Ubangi (35 cases / 2 deaths) and Bikoro, in Ecuador (21 cases / 0 deaths),” says the Monkeypox coordination report.
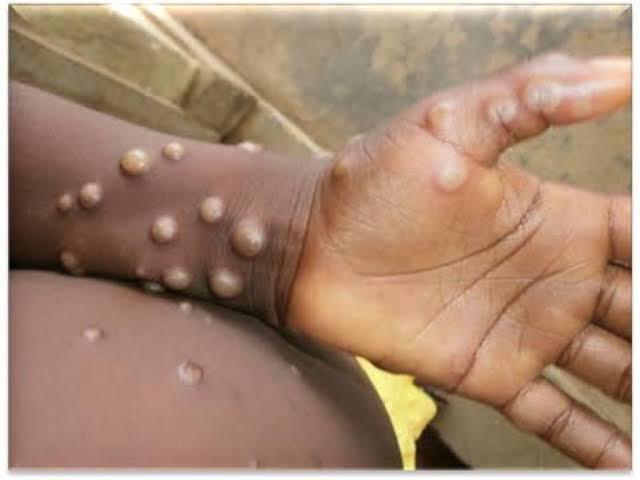
According to this branch of the Ministry of Public Health, Hygiene and Prevention, children under 15 are the most affected. They represent 70% of suspected cases and 87% of deaths. The accumulation of cases over the years shows that in 2022, 5,697 suspected cases were reported, with 234 deaths (4.1%); in 2023, 14,626 suspected cases, and 654 deaths (4.46%); and in 2024 (S1-S8): 4,169 suspected cases; 279 deaths (6.7%).
The National Institute of Public Health (INSP) in collaboration with the Ministry of Health and some organizations in the health sector proceeded on Tuesday, February 27 to develop a response plan for the Monkeypox epidemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Therese Ntumba
Outbreak of suspected cases of Monkeypox in the DRC: more than 220 notifications in one week
Wednesday March 27, 2024 - 2:53 p.m.
The Monkeypox coordination of the Ministry of Health specified in its report that it had notified 228 new suspected cases of Monkeypox during epidemiological week 11 (March 15 to 22, 2024).
“228 new suspected cases and 8 deaths reported (case fatality = 3.5%) in SE 11 of 2024. Seven out of 27 provincial health divisions reported cases, or 27%. The ZS of Lotumbe in the province of Équateur reported the highest number of cases in S11, i.e. 85 cases and 1 death (case fatality = 1.2%), followed by Budjala, in Sud-Ubangi (35 cases / 2 deaths) and Bikoro, in Ecuador (21 cases / 0 deaths),” says the Monkeypox coordination report.
According to this branch of the Ministry of Public Health, Hygiene and Prevention, children under 15 are the most affected. They represent 70% of suspected cases and 87% of deaths. The accumulation of cases over the years shows that in 2022, 5,697 suspected cases were reported, with 234 deaths (4.1%); in 2023, 14,626 suspected cases, and 654 deaths (4.46%); and in 2024 (S1-S8): 4,169 suspected cases; 279 deaths (6.7%).
The National Institute of Public Health (INSP) in collaboration with the Ministry of Health and some organizations in the health sector proceeded on Tuesday, February 27 to develop a response plan for the Monkeypox epidemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Therese Ntumba






 Download Report
Download Report

 Download Report
Download Report
Comment