July 7 2021
JingLu
Baisheng Li1,2#, Aiping Deng1,2#, Kuibiao Li3#, Yao Hu1,2#, Zhencui Li1,2#, Qianling Xiong1,2,4, Zhe Liu1,2, Qianfang Guo1,2, Lirong Zou1,2, Huan Zhang1,2,Meng Zhang1,2, Fangzhu Ouyang1,2, Juan Su1,2, Wenzhe Su3, Jing Xu1,2, Huifang Lin1,2,4, Jing Sun1,2,4, Jingju Peng1,2,4, Huiming Jiang1,2,4, Pingping Zhou1,2,4, Huanying Zhen1,2, Jianpeng Xiao1,2,4, Tao Liu1,2,4, Rongfei Che1,2, Hanri Zeng1,2, Zhonghua Zheng1,2, Yushi Huang1,2, Jianxiang Yu1,2, Lina Yi1,2,4, Jie Wu1,2, Jingdiao Chen1,2, Haojie Zhong1,2, Xiaoling Deng1,2, Min Kang1,2, Oliver G. Pybus5, Matthew Hall6, Katrina A. Lythgoe6, Yan Li1,2*, Jun Yuan3*, Jianfeng He1,2*, Jing Lu1,2,4*
Summary
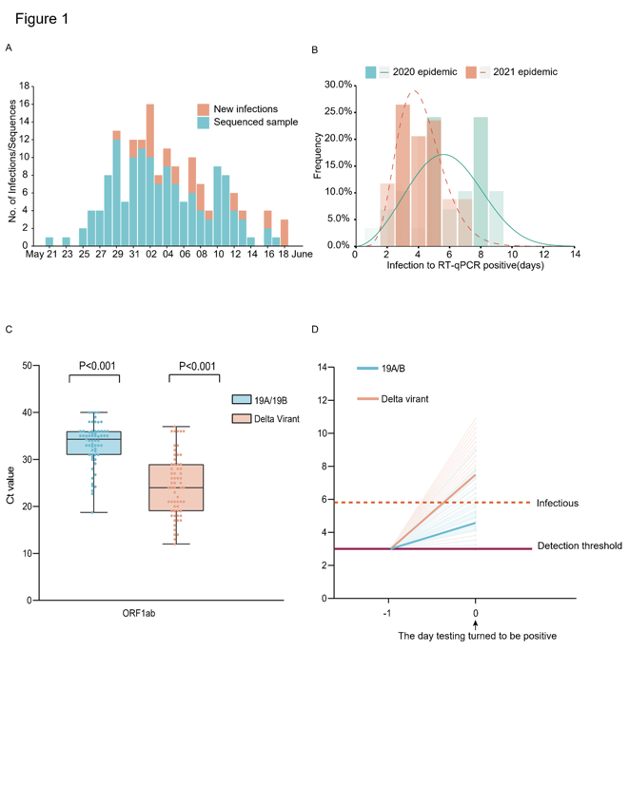
We report the first local transmission of the Delta SARS-CoV-2 variant in mainland China. All 167 infections could be traced back to the first index case. The investigation on daily sequential PCR testing of the quarantined subjects indicated the viral load of the first positive test of Delta infections was ~1000 times higher than that of the 19A/19B strains infections back in the initial epidemic wave of 2020, suggesting the potential faster viral replication rate and more infectiousness of the Delta variant at the early stage of the infection. The 126 high-quality sequencing data and reliable epidemiological data indicated some minor intra-host single nucleotide variants (iSNVs) could be transmitted between hosts and finally fixed in the virus population during the outbreak. The minor iSNVs transmission between donor-recipient contribute at least 4 of 31 substitutions identified in the outbreak suggesting some iSNVs could quickly arise and reach fixation when the virus spread rapidly. Disease control measures, including the frequency of population testing, quarantine in pre-symptomatic phase and enhancing the genetic surveillance should be adjusted to account for the increasing prevalence of the Delta variant at global level.
During the global spread of SARS-CoV-2, the genetic variants of the viruses emerged, and some have been proved to be more transmissible or could escape from the host immunity, which posed an increased risk to global public health1–3. An emerging genetic lineage, B.1.617, has been dominant in the largest outbreak of COVID-19 in India since March 2021, gaining global attention. One sublineage, B.1.617.2, with spike protein mutations L452R, T478K and P681R, accounts for ~28% sequenced cases in Indian and rapidly replaced other lineages to become dominant in multiple regions and countries (https://outbreak.info/ 11)4. The B.1.617.2 has been labeled as Variant of Concern (VOC), Delta (https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants 17). The virological profile of this VOC is needed to be urgently illustrated. ...
On May 21, 2021 the first local infection of the Delta variant in mainland China was identified.
JingLu
Baisheng Li1,2#, Aiping Deng1,2#, Kuibiao Li3#, Yao Hu1,2#, Zhencui Li1,2#, Qianling Xiong1,2,4, Zhe Liu1,2, Qianfang Guo1,2, Lirong Zou1,2, Huan Zhang1,2,Meng Zhang1,2, Fangzhu Ouyang1,2, Juan Su1,2, Wenzhe Su3, Jing Xu1,2, Huifang Lin1,2,4, Jing Sun1,2,4, Jingju Peng1,2,4, Huiming Jiang1,2,4, Pingping Zhou1,2,4, Huanying Zhen1,2, Jianpeng Xiao1,2,4, Tao Liu1,2,4, Rongfei Che1,2, Hanri Zeng1,2, Zhonghua Zheng1,2, Yushi Huang1,2, Jianxiang Yu1,2, Lina Yi1,2,4, Jie Wu1,2, Jingdiao Chen1,2, Haojie Zhong1,2, Xiaoling Deng1,2, Min Kang1,2, Oliver G. Pybus5, Matthew Hall6, Katrina A. Lythgoe6, Yan Li1,2*, Jun Yuan3*, Jianfeng He1,2*, Jing Lu1,2,4*
Summary
We report the first local transmission of the Delta SARS-CoV-2 variant in mainland China. All 167 infections could be traced back to the first index case. The investigation on daily sequential PCR testing of the quarantined subjects indicated the viral load of the first positive test of Delta infections was ~1000 times higher than that of the 19A/19B strains infections back in the initial epidemic wave of 2020, suggesting the potential faster viral replication rate and more infectiousness of the Delta variant at the early stage of the infection. The 126 high-quality sequencing data and reliable epidemiological data indicated some minor intra-host single nucleotide variants (iSNVs) could be transmitted between hosts and finally fixed in the virus population during the outbreak. The minor iSNVs transmission between donor-recipient contribute at least 4 of 31 substitutions identified in the outbreak suggesting some iSNVs could quickly arise and reach fixation when the virus spread rapidly. Disease control measures, including the frequency of population testing, quarantine in pre-symptomatic phase and enhancing the genetic surveillance should be adjusted to account for the increasing prevalence of the Delta variant at global level.
During the global spread of SARS-CoV-2, the genetic variants of the viruses emerged, and some have been proved to be more transmissible or could escape from the host immunity, which posed an increased risk to global public health1–3. An emerging genetic lineage, B.1.617, has been dominant in the largest outbreak of COVID-19 in India since March 2021, gaining global attention. One sublineage, B.1.617.2, with spike protein mutations L452R, T478K and P681R, accounts for ~28% sequenced cases in Indian and rapidly replaced other lineages to become dominant in multiple regions and countries (https://outbreak.info/ 11)4. The B.1.617.2 has been labeled as Variant of Concern (VOC), Delta (https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants 17). The virological profile of this VOC is needed to be urgently illustrated. ...
On May 21, 2021 the first local infection of the Delta variant in mainland China was identified.